-
Aggregation
- Combine data objects to convert it into a higher resolution
-
Sampling
-
Take a random subset of data from the entire population
-
A sample is representative if it represents the same statistics as the original data
-
Simple Random Sampling
-
Take out a random sample from the entire dataset
-
Sampling With Replacement
- Put the taken object back into the population
-
Sampling Without Replacement
- Take out the object and do not put back into the population
-
-
Stratified Sampling
- Split the data into several partitions; then draw random samples from each partition
-
-
Discretisation
- AKA Binning
- Process of putting continuous values into buckets so that there are a limited number of possible states
-
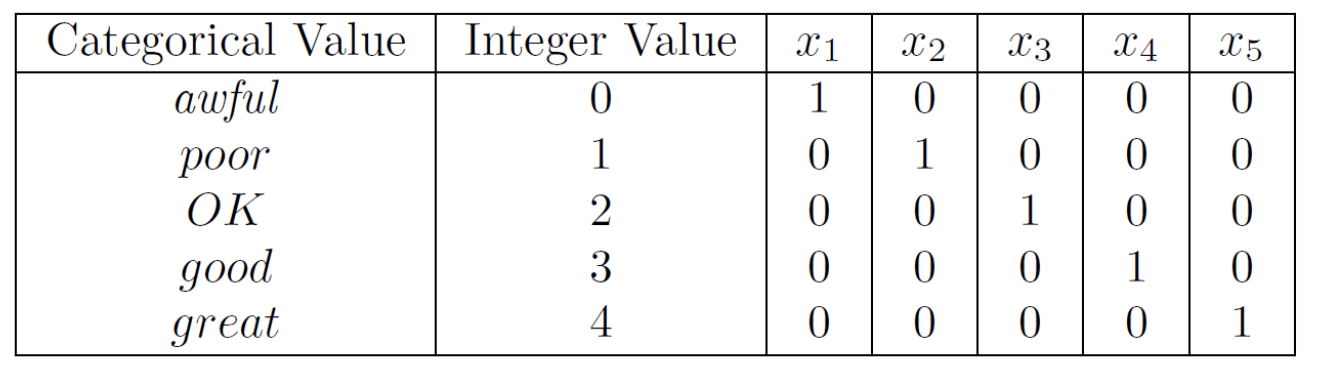
Binarisation
-
Process of converting numerical or categorical data into binary values
0 or1 based on a certain threshold
-
-
Attribute Transformation
-
Normalisation
- Refers to various techniques to adjust to differences among attributes in terms of frequency of occurrence, mean, variance, range
-
Standardisation
-
Reshape the data to form a bell curve
- Mean = 0
- Std. = 1
-
-
-
Dimensionality Reduction
-
Remove Irrelevant Features
-
Allow data to be more easily visualised
-
Avoid Curse of Dimensionality
- When dimensionality increases, data becomes increasingly sparse in the space that it occupies
-
Techniques
-
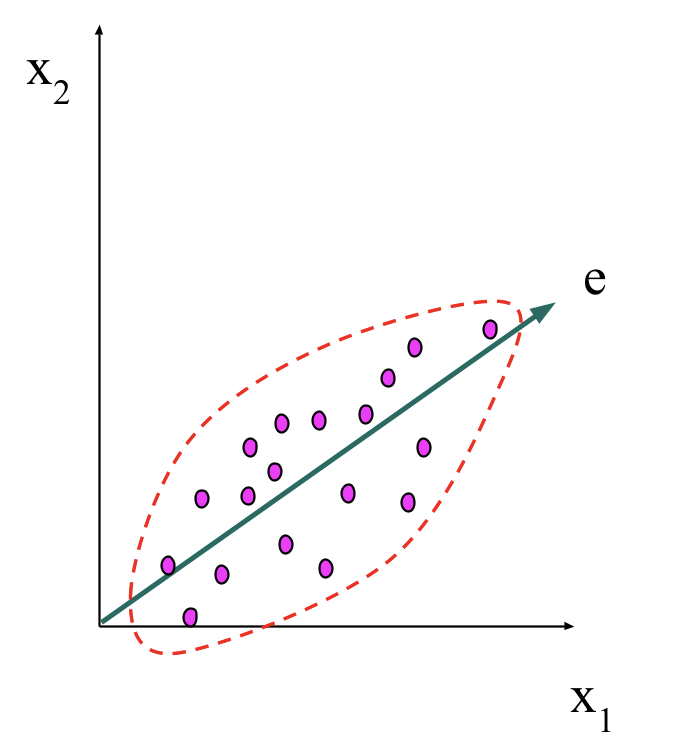
PCA
-
Find a projection that represents the largest amount of variation in the data
-
-
Feature Subset Selection
- Remove Redundant Features
- Remove Irrelevant Features
-
Mapping Data to New Space
- Fourier Transformation
- Wavelet Transformation
-
-

