Using Naive Bayes and N-Gram for Document Classification
Bayesian Rule
Assumption
Attribute variables are conditionally independent from each other given / provided the class / target variable
Language Model
Naive Bayes is also used as a popular Language Model
The parameters are found during the training phase
Algorithm
- Calculate Prior from the documents given
- Create a unified Vocabulary
- Create a Mega Document for each class which concatenates the documents / sentences of each instance of the class
Smoothing
Apply Smoothing Techniques to deal with zero probabilities
Unknown
Unknown words can simply be removed since they don’t contribute much to the performance
Stop Words
Removing stop words don’t improve and contribute that much to the performance but still its a common practice to remove the top 10 most frequent words considering as stop words since they don’t really help in classification related tasks
Example
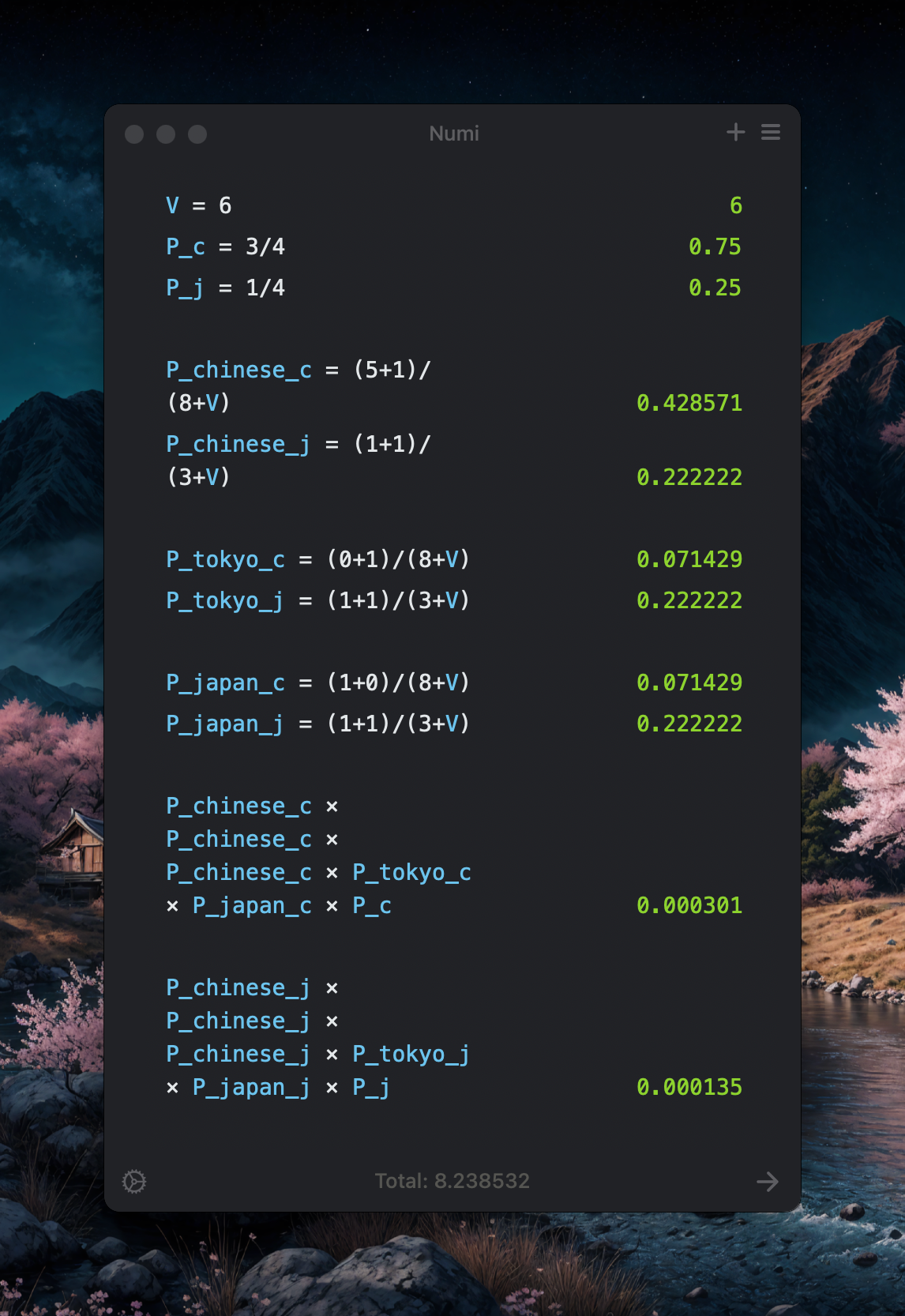
Pros
- Robust to Isolated Noise Points
- Robust to irrelevant attributes
- Can handle missing values by ignoring the instance (such as ) during probability calculation
Shortcomings
-
If used as a Language Model:
- Context is lost since we assume conditional independence
- Positioning of words are neglected and thus semantics are lost
Redundant and correlated attributes will violate the class conditional assumption of Naive Bayes. We use other techniques such as Bayesian Belief Networks to overcome this.

