- Business Idea
- Concept for a new product or service that would add to the innovation
- Originates from imagination
- Business Opportunity
- Concept for a new product or service that would be able to address the current gaps in the market
- Originates from potential gaps that can be exploited
- Four Qualities of an Opportunity
- Timely
- Durable
- Attractive
- Value
- Identify an Opportunity by:
- Observing Trends
- Mobile phone was created and rose to fame because of human travels and mobility
- Solving Problems
- Wind Farms were made to solve the increasing wind blowing problems and generate electricity through them at the same time
- Gaps in the Market
- Entrepreneurial Alertness
- A “sixth sense” that allows them to see opportunities that others miss
- Weak-tie Relationship can lead to more new business ideas than Strong-tie Relationship
- This is because in Weak-tie Relationship, one may say something to another that sparks a completely new idea
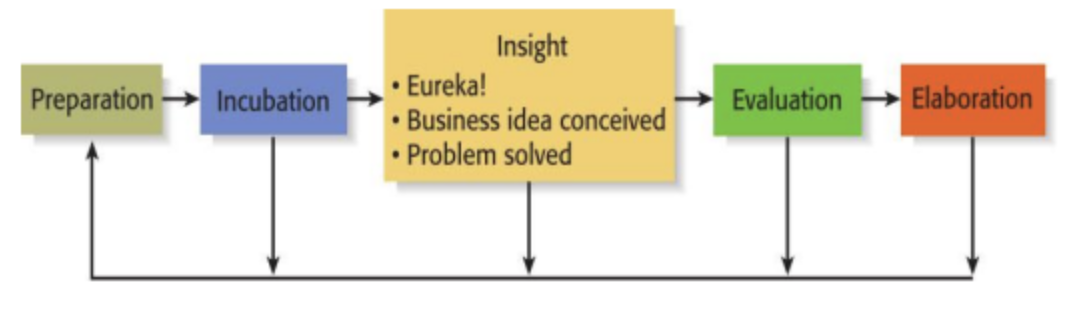
- Creative Process of an Individual
- Preparation
- Incubation
- Insight
- Evaluation
- Elaboration
- Techniques to Generate Ideas
- Brainstorming
- Focus Group
- Library and Internet Research
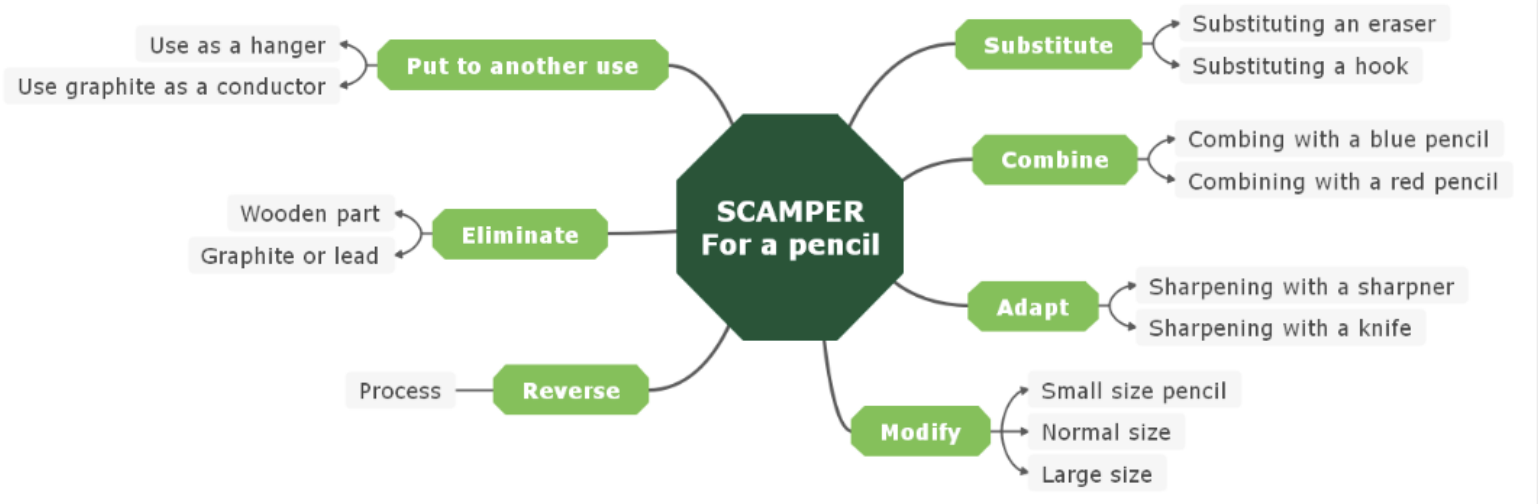
- SCAMPER
- Technique that assists in introducing changes to existing products to create a new one
- Consists of:
- S - Substitute
- Replace a part, material with something else
- C - Combine
- Add new parts or materials
- A - Adapt
- Modify the product to suit a new purpose
- M - Modify
- Enlarge, reduce or change shape if the
- P - Put to another use
- Put product to another using without changing it
- E - Eliminate
- Remove elements and reduce to essential parts
- R - Reverse
Lecture 3
- Feasibility analysis is the process of determining if a business idea is viable
- Proper time to conduct a feasibility analysis is early in thinking
- 4 Types of Feasibility Analysis
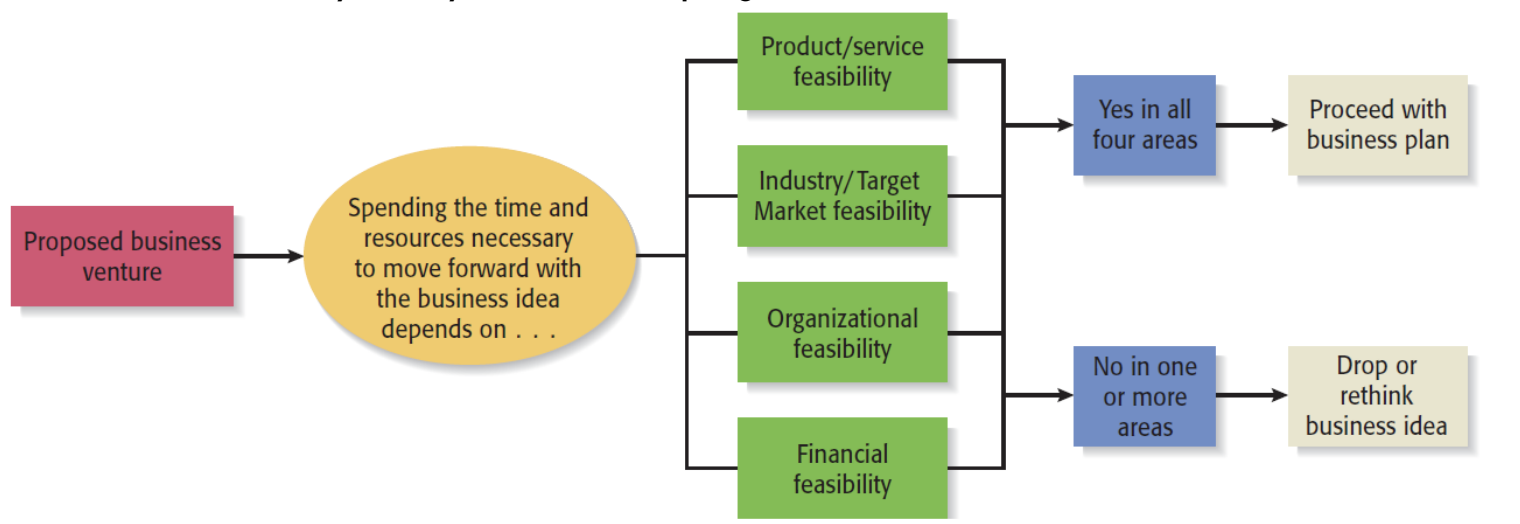
- Product/Service Feasibility
- Product/Service Desirability
- Does the product makes sense and solves a particular problem. Will someone be willing to use it?
- Product/Service Demand
- Talking face-to-face with customers to see if you’re making what they actually need
- Using online tools such as Google Keywords etc to understand the current trends and demands
- Surveys and Forums can also help
- Industry/Target Market Feasibility
- Industry is a group of firms making similar products
- Industry Attractiveness
- Younger industries are preferred
- Early in their lifecycle
- Are fragmented rather than concentrated
- Concentrated industries are industries with dominant players
- Are growing rather than sinking
- Target Market Attractiveness
- Find a market that’s large enough for the proposed business but is yet small enough to avoid attracting larger competitors.
- Organizational Feasibility
- Management Prowess
- Ability of an organization’s management team to satisfy the organization that management has the requisite passion and expertise to launch the venture
- Resource Sufficiency
- Availability of space, employee and contractors etc
- Management team and Company Structure
- Should consist of founder(s) and key management persons
- Organizational Chart
- Operations Plan
- How the business will be run and how the product or service will be produced
- Product/Service Design and Development Plan
- If product then prototype should be designed initially
- Financial Feasibility
- Total Start-Up Cash Needed
- List down the resources
- Estimate the Cost of Listed Resources
- Decide about Debt and Equity Financing
- Boot Scrapping
- Process of building a business from scratch without attracting investment or with minimal external capital
- Financial Performance of Similar Businesses
- Estimate financial performance by comparing to similar, already established businesses.
- Overall Financial Attractiveness of the Proposed Investment
- Ability to forecast income and expenses with a reasonable degree of certainty
- Internally generated funds to finance and sustain growth
- Availability of an exit opportunity for investors to convert equity to cash
- Crowd Funders
- Reward based Crowd funding platforms help to raise funding to build a prototype and market test a great idea or product
- If a business idea passes the Feasibility Analysis, the next step is to complete a business plan
Lecture 4
- Business Model
- A company’s plan for making a profit
- The proper time to develop a business model is following the feasibility analysis stage and prior to fleshing out the operational details
- Classes/Classification of Business Model
- Categories of Business Model
- Standard Business Model
- Existing plans or recipes firms can use to determine how they will create, deliver, and capture value
- Some of these Business Models include:
- Advertising Business Model
- Auction Business Model
- Bricks and Clicks BusinessModel
- Franchise Business Model
- Freemium Business Model
- Low-Cost Business Model
- Manufacturer/Retailer Business Model
- Peer-to-Peer Business Model
- Razor and Blades Business Model
- Subscription Business Model
- Traditional Retailer Business Model
- Disruptive Business Models
- They are impactful enough that they disrupt or change the way business is conducted in an industry or an important niche within an industry
- Barringer/Ireland Business Model Template
- A template for crafting a Business Model
- Consists of 12 elements divided into 4 categories
- Following are the categories along with their elements:
- Core Strategy
- Describes how the firm plans to compete relative to its competitors
- Business Mission
- Why it exists and what its business model is supposed to accomplish
- Basis of Differentiation
- Basis of differentiation is what causes consumers to pick one company’s products over another’s
- Target Market
- Which sector will your product target?
- Product/Market Scope
- How do you plan to expand to your target market?
- Resources
- Core Competency
- A specific factor or resource that supports a firm’s business model and sets it apart from rivals
- Key Assets
- Assets that a firm owns that enable its business model to work
- Could be physical, financial, intellectual, or human
- Financials
- Revenue Streams
- Describe the ways in which it makes money
- Can be a single or many streams
- Cost Structure
- Cost analysis
- Cost-driven or value-driven?
- Financing/Funding
- Indicate the appropriate amount of funding that will be needed and where the money will most likely come from
- Operations
- Product/Service Production
- how a firm’s products and/or services are produced
- Channels
- Describe how it delivers its product or service to its customers
- Key Partners
- Partnerships formed to achieve a goal
- Following types of partnerships can be formed:
- Joint venture
- Network
- Consortia
- Strategic alliance
- Trade associations





