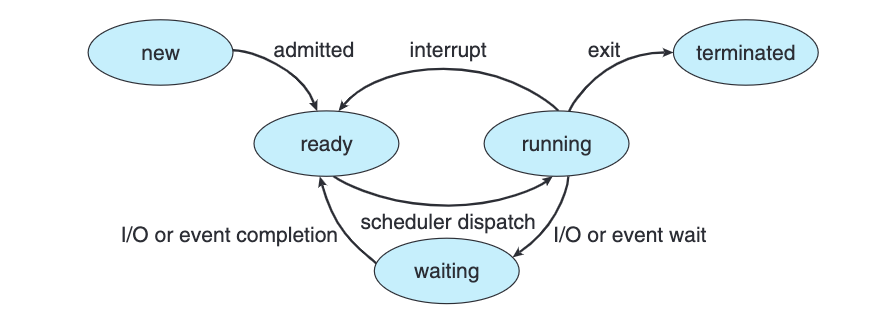
New State
- Jobs are called programs here
- Waiting in the hard disk for memory allocation
- Linking and Loading is still yet to be done
- Program is waiting to be converted into a process / Allocate a Process Control Block
Job Queue
- The programs which are still yet to be converted to a process are waiting here
Long-Term / Job Scheduler
-
Schedules jobs from the job queue to be put into the main memory
-
Long-term scheduler is invoked infrequently (seconds, minutes) → (may be slow)
-
Manages the Degree of Multiprogramming
- Keeps track of the count of available space in the memory to load processes
- A mixture of I/O bound and CPU Bound processes are selected to be loaded in the memory
Ready State
- Loaded in the main memory waiting to be executed
Ready Queue
- The multiple processes which are yet to be executed are queued here
Short-Term / CPU
- Schedules processes from ready queue to be executed into the CPU
- Short-term scheduler is invoked frequently (milliseconds) → (must be fast)
- Algorithms should be devised from the number of processes available in the ready queue such that the throughput of the CPU can be maximum
Running State
- The process is executed in the CPU in here
Migrations from Running to Ready Stage
- Interrupts between processing
- Based on Scheduling Time
Waiting State
- If a process while in running stage requires an I/O event to occur then it is put into this stage
- Process requesting I/O operations are put here
Device Queue
- Multiple requests to use a specific device are put here
On the completion of that specific I/O operation, the state of the process is transitioned to Ready State
Exit State
- If a process is completed entirely then it is put here