Part of the secondary memory that helps in increasing the size of the virtual memory
In intuition, suspended processes reside in the virtual memory
Demand Paging
If there’s a process page that could not be located in the Main Memory, then we will need to find it in the Virtual Memory or other sources
- If the page is found in the page table, we have a page hit. Else we have a page miss and there’s a need to search for that page in the virtual memory
Reasons Page Could not be Found
- Main Memory is full and we cannot find a frame for the page to be allocated
- That specific page was swapped out as suspended as in the 7 State Process Model
Modification in Page Table
Another column Valid is added to the Page Table for determining validity of the Page, i.e if its loaded into the Main Memory Frames or Not
| Frame # | Valid |
|---|---|
| 120 | 1 |
| - | 0 |
- If
Valid = 0, the Page is not available in the memory - If
Valid = 1, the Page is available somewhere in the memory
Performance
Page Fault Rate
The percentage / probability we will be able to find the page in the Page Table
Effective Access Time
Demand paging can significantly affect the performance of a computer system and Effective Access Time helps us in computing it’s performance
-
Swap In Cost is the cost of bringing in the pages into the memory from Virtual Memory -
Swap Out Cost is added if the memory was full and there a need to create some space
Steps in handling a page fault.
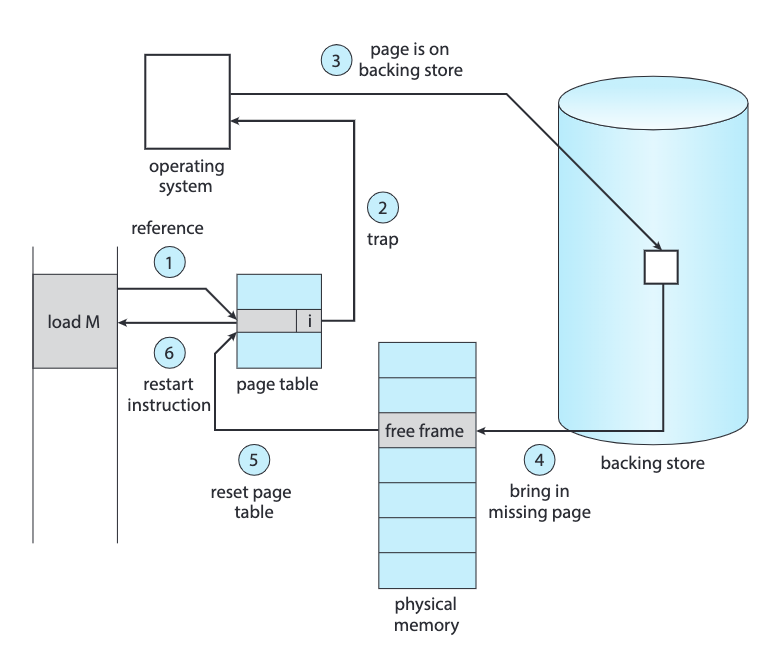
Example
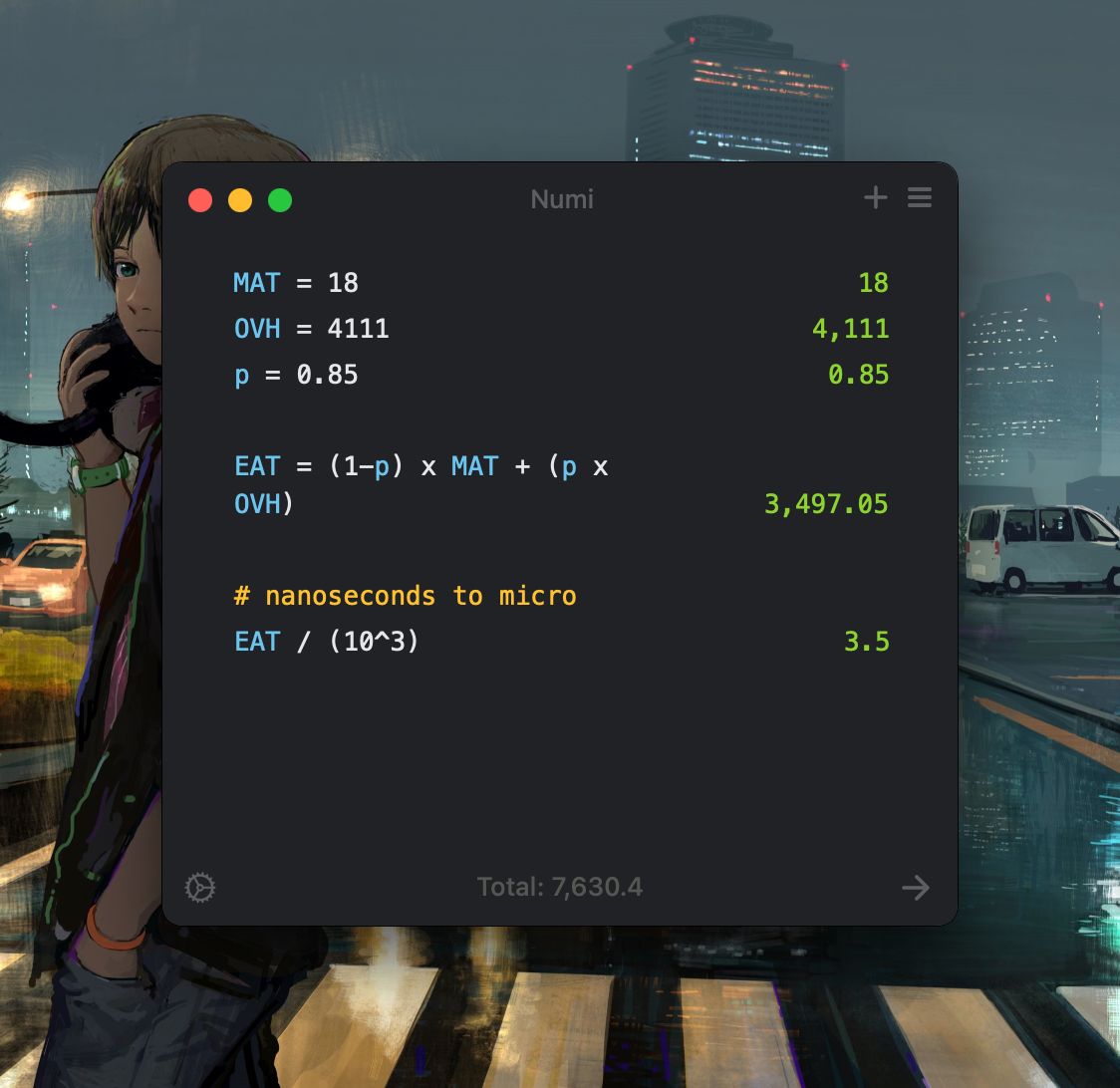
Question 6 (5 points): If memory access time is equal to the year you enrolled in FAST. e.g. 18 nanoseconds, and page fault overhead time is equal to your registration number, e.g. 4111 nanoseconds. If the probability of having a page fault is 0.85, then calculate the Effective Access Time. Here, the page fault overhead time also includes the page swap in and swap out time.
Page Replacement Policies
The criteria of selecting the page that needs to be swapped out to create space for a page demand can vary and thus we can come up with different policies
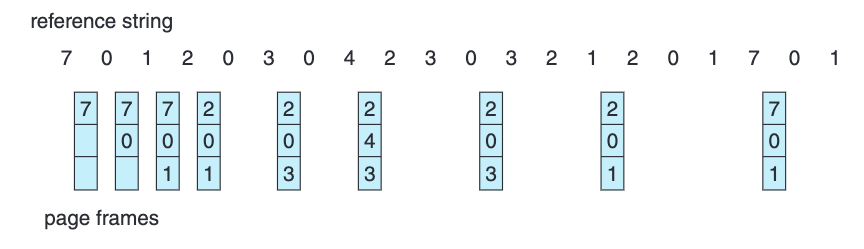
FIFO
First in First Out Structure
The page which was came the oldest into the memory, i.e which came first and has the longest time in the main memory, will be replaced and swapped out
FIFO page-replacement algorithm
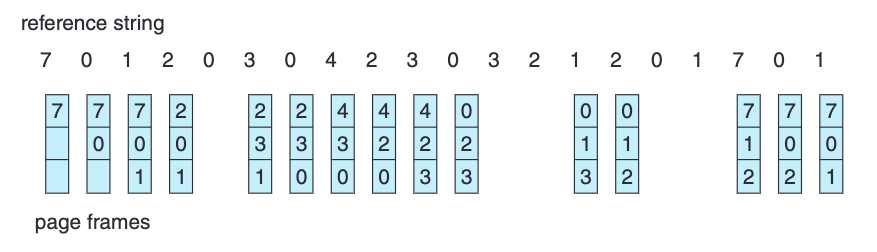
LRU
Least Recently Used
We keep those pages into the memory that are frequently used and discard those which are used least frequently
- LRU looks in the previous pages which were demanded in the reference string
LRU page-replacement algorithm
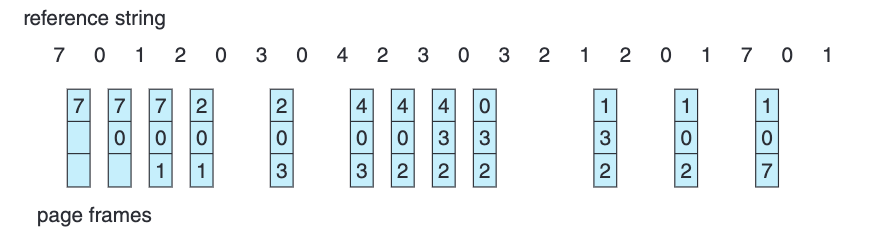
Optimal Algorithm
Look into the Future / Far into the Reference string given that we have the complete reference string, and determine page will be least frequently used in the future and discard that page