Reference Document: A 2.pdf
Q1
Write an OpenMP program that should create 8 threads to run in parallel and display thread id of each created thread.
#include <iostream>
#include <omp.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(8)
cout << omp_get_thread_num();
return 0;
}Q2
#include <iostream>
#include <omp.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int nums[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
omp_set_num_threads(3);
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(static, 3)
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
nums[j] *= (j+3);
int x = omp_get_thread_num();
cout << "At thread: " << x << " iteration: ";
cout << j << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Output
At thread: 0 iteration 0
At thread: 0 iteration 1
At thread: 0 iteration 2
At thread: 1 iteration 3
At thread: 1 iteration 4
At thread: 1 iteration 5
At thread: 2 iteration 6
At thread: 2 iteration 7
At thread: 2 iteration 8
At thread: 0 iteration 9
3 8 15 24 35 48 63 80 99 120
Q3
Can you describe the use of the following terms or clauses in OpenMP:
a) lastprivate(var)
The lastprivate(var) clause in OpenMP is used to tell the compiler to copy the result of the last thread that will be working on the variable var to the same global or overall system variable
b) schedule(static, 4)
The schedule(static, 4) clause is used by OpenMP to dictate the order in which iterations are split and assigned to the threads. According to this static clause, the iterations should be split into chunks of size 4. These chunks are then further assigned to the threads for processing in a round robin fashion.
Q4
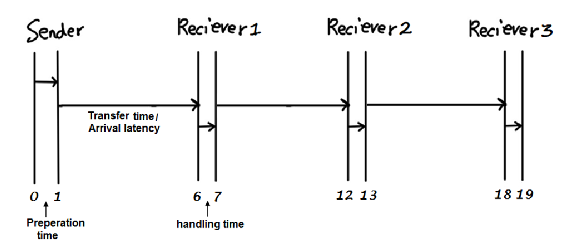
Calculate the total communication cost required to transfer 400 mbits of data from Sender to Receiver3. Bandwidth of the link is 10 mbits/s.
Store and forward routing
Packet routing
Cut through routing: tw = 0.01
Since = then Bandwidth = mbits/s